










Color
While many diamonds appear colorless, or white, they may actually have subtle yellow or brown tones that can be detected when comparing diamonds side by side. Colorless diamonds are the rarest and most valuable of all. Color variations are a result of the natural forces (i.e., temperature, pressure, trace elements) at work during the formation of diamonds within the Earth. Because subtle color variations dramatically affect the value of a diamond, a color grading scale is used to categorize the shading differences
This blog is in complete
 The Pear cut is a tear-drop shape and is a variation of the round brilliant cut diamond. This attractive diamond is also extremely well-suited to pendants and earrings. Many of the largest stones ever discovered have been cut and faceted into magnificent pear-shapes.
The Pear cut is a tear-drop shape and is a variation of the round brilliant cut diamond. This attractive diamond is also extremely well-suited to pendants and earrings. Many of the largest stones ever discovered have been cut and faceted into magnificent pear-shapes.
A hybrid cut, combining the best of the oval and the marquise, it is shaped most like a sparkling teardrop
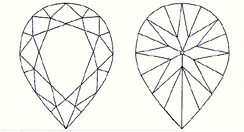 Length to width ratio: Most people prefer a pear-shaped diamond to have a length to width ratio of approximately 1.65:1. More elongated pear-shapes extend to a ratio of 1.80:1, whereas a more compact look is achieved with a ratio closer to 1.20:1
Length to width ratio: Most people prefer a pear-shaped diamond to have a length to width ratio of approximately 1.65:1. More elongated pear-shapes extend to a ratio of 1.80:1, whereas a more compact look is achieved with a ratio closer to 1.20:1
 The ultimate symbol of love, the romantic Heart shape is a variation of the round brilliant cut diamond. This ultimate symbol of romance is essentially a pear-shaped diamond with a cleft at the top. The skill of the cutter determines the beauty of the cut. Look for a stone with an even shape and a well-defined outline.
The ultimate symbol of love, the romantic Heart shape is a variation of the round brilliant cut diamond. This ultimate symbol of romance is essentially a pear-shaped diamond with a cleft at the top. The skill of the cutter determines the beauty of the cut. Look for a stone with an even shape and a well-defined outline.
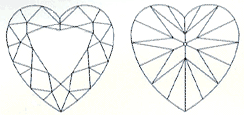 Length to width ratio: A heart-shaped stone is usually proportioned with equal length and width, approximating a ratio of 1:1. A length to width ratio of between 0.90:1 and 1.15:1 is preferred. The ratio should not fall below 0.80:1 or exceed 1.20:
Length to width ratio: A heart-shaped stone is usually proportioned with equal length and width, approximating a ratio of 1:1. A length to width ratio of between 0.90:1 and 1.15:1 is preferred. The ratio should not fall below 0.80:1 or exceed 1.20:
 The Oval cut is elliptical in shape and is a variation of the round brilliant cut diamond. The oval shaped diamond gives a flattering illusion of length to the finger and hand, and is popular among women with small hands or short fingers. It can also accentuate long, slender fingers.
The Oval cut is elliptical in shape and is a variation of the round brilliant cut diamond. The oval shaped diamond gives a flattering illusion of length to the finger and hand, and is popular among women with small hands or short fingers. It can also accentuate long, slender fingers.
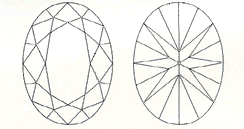 Length to width ratio: An oval cut with a length to width ratio of approximately 1.40 - 1.60 is the preference of most diamond buyers. For those who prefer a rounder look, choose a ratio closer to 1.15:1. For those who prefer a more elongated shape, look for a ratio of 1.70:1
Length to width ratio: An oval cut with a length to width ratio of approximately 1.40 - 1.60 is the preference of most diamond buyers. For those who prefer a rounder look, choose a ratio closer to 1.15:1. For those who prefer a more elongated shape, look for a ratio of 1.70:1
Shapes of Diamonds - Asscher
 The Asscher cut is a variant of the emerald cut and provides a uniquely regal and elegant look to its wearer. Its art-deco styling combines old-world charm with modern cutting and faceting techniques to produce a dazzling example of brilliance.
The Asscher cut is a variant of the emerald cut and provides a uniquely regal and elegant look to its wearer. Its art-deco styling combines old-world charm with modern cutting and faceting techniques to produce a dazzling example of brilliance.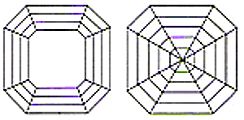 Length to width ratio: Very Square Asscher cuts (Ratio of 1:1) are prefered to even slightly more rectangular looking ones. Asscher cuts should not exceed a ratio of 1.1:1.
Length to width ratio: Very Square Asscher cuts (Ratio of 1:1) are prefered to even slightly more rectangular looking ones. Asscher cuts should not exceed a ratio of 1.1:1.
This is a brilliant-cut triangle diamond - a wedge shape with fiery brilliance. It can be a traditional triangular shape with pointed corners, or a more rounded triangular shape. Trillions (also called Trilliants or Triangles) are often used as diamond accents in three stone rings and other jewelry settings, but may also be chosen to be set as solitaire diamonds.
This is a spectacular wedge of brittle fire. First developed in Amsterdam, the exact design can vary depending on a particular diamond's natural characteristics and the cutter's personal preferences. It may be a traditional triangular shape with pointed corners or a more rounded triangular shape with 25 facets on the crown, 19 facets on thepavilion, and a polished girdle. It is definitely for the adventurous.
Length to width ratio: An equilateral triangle is prefered in a trillion diamond. Variance in the ratio of length to width should not deviate considerably.
 This is a modified or combination cut - a brilliant cut square or rectangle shaped diamond with clipped-off corners like the emerald cut. It melds the elegance of the emerald cut diamond with the brilliance and sparkle of the round diamond.
This is a modified or combination cut - a brilliant cut square or rectangle shaped diamond with clipped-off corners like the emerald cut. It melds the elegance of the emerald cut diamond with the brilliance and sparkle of the round diamond.
This square or rectangular cut combines the elegance of the emerald shape diamond with the brilliance of the round, and its 70 facets maximize the effect of its color refraction. Because of its design, this cut requires more weight to be directed toward the diamond's depth in order to maximize brilliance. Depth percentages of 70% to 78% are not uncommon.
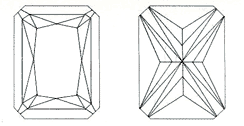 Length to width ratio: A radiant cut with a length to width ratio of less than or equal to 1.05:1 will appear square to the observer. While a squarer radiant-cut diamond is the preference of many, some people prefer a slightly rectangular diamond.
Length to width ratio: A radiant cut with a length to width ratio of less than or equal to 1.05:1 will appear square to the observer. While a squarer radiant-cut diamond is the preference of many, some people prefer a slightly rectangular diamond.
 The Marquise cut is boat shaped and is a variation of the round brilliant cut diamond. Marquise cuts are often chosen by women who wish to display an independence of style. Its elongated form can create the illusion of longer, narrower fingers.
The Marquise cut is boat shaped and is a variation of the round brilliant cut diamond. Marquise cuts are often chosen by women who wish to display an independence of style. Its elongated form can create the illusion of longer, narrower fingers.
An elongated shape with pointed ends inspired by the fetching smile of the Marquise de Pompadour and commissioned by the Sun King, France's Louis XIV, who wanted a diamond to match it. It is gorgeous when used as a solitaire or when enhanced by smaller diamonds.
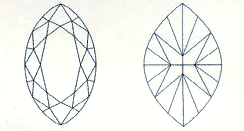 Length to width ratio: A marquise cut with a length to width ratio of approximately 2:1 is the norm. For those who prefer a rounder look, choose a ratio closer to 1.5:1. For those who prefer a more elongated shape, look for a ratio of 2.25:
Length to width ratio: A marquise cut with a length to width ratio of approximately 2:1 is the norm. For those who prefer a rounder look, choose a ratio closer to 1.5:1. For those who prefer a more elongated shape, look for a ratio of 2.25:
 The Emerald cut is rectangular with cut corners. It is a step cut - its facets being broad with flat planes resembling the steps of a stair. Higher quality Emerald cuts are preferred because its cut makes inclusions and lower color grades more noticeable than with other cuts.
The Emerald cut is rectangular with cut corners. It is a step cut - its facets being broad with flat planes resembling the steps of a stair. Higher quality Emerald cuts are preferred because its cut makes inclusions and lower color grades more noticeable than with other cuts.
The emerald cut diamond can be absolutely stunning. Because of it's long lines, it tends to be less fiery than a "round brilliant" cut, but it also tends to have broader, more dramatic flashes of light. The trim lines of emerald cut diamonds lend an elegant, sophisticated air to both the simplest and most elaborate ring settings.
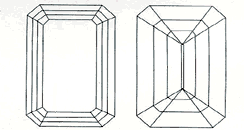 When purchasing an emerald cut diamond, it's extremely important to pay attention to quality and to select the highest grade stone you can afford. Because of the "openess" of the cut, flaws, color weakness, and a poor cut are more evident to the naked eye than a cut such as the round brilliant. The good news is, emerald cut diamonds are not as "traditional" as the round brilliant or as trendy as the princess cut -- making their pricing extremely economical when compared to the more common cuts.
When purchasing an emerald cut diamond, it's extremely important to pay attention to quality and to select the highest grade stone you can afford. Because of the "openess" of the cut, flaws, color weakness, and a poor cut are more evident to the naked eye than a cut such as the round brilliant. The good news is, emerald cut diamonds are not as "traditional" as the round brilliant or as trendy as the princess cut -- making their pricing extremely economical when compared to the more common cuts.
Length to width ratio: An emerald cut with a length to width ratio of approximately 1.35:1 is generally the most prized. However, in recent years, square emerald cuts have become extremely popular.
 The Cushion Cut diamond is an antique style that is a blend of several different shapes including round, oval and princess. It can be found in either square or rectangular shapes and is often referred to as a pillow-cut for it resembles an overstuffed pillow or cushion.
The Cushion Cut diamond is an antique style that is a blend of several different shapes including round, oval and princess. It can be found in either square or rectangular shapes and is often referred to as a pillow-cut for it resembles an overstuffed pillow or cushion.
Cushion cut diamonds initially gained popularity during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. At the time, they were commonly referred to as Candlelight Cuts due to the fact they were cut in such a way as to maximize brilliance under candlelit conditions, as the light bulb did not yet exist.
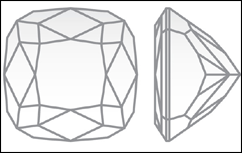 The Cushion Cut has fewer facets than most other shapes and the facets are larger, so with this shape importance as inclusions will be more easily visible to the naked eye.
The Cushion Cut has fewer facets than most other shapes and the facets are larger, so with this shape importance as inclusions will be more easily visible to the naked eye.
Length to width ratio: A cushion cut with a length to width ratio of less than or equal to 1.05:1 will appear square to the observer. While a squarer diamond is the preference of many, some people prefer a slightly rectangular-shaped cushion diamond with length to width ratios of 1.15:1 to 1.30:1.
 The Princess cut is a square cut with sharp edges. It has very good fire and a high degree of brilliance. The princess cut utilizes most of the original shape of the rough diamond and the weight loss from cutting is low. As a result, its price is usually more attractive than a comparative round cut with the same weight.
The Princess cut is a square cut with sharp edges. It has very good fire and a high degree of brilliance. The princess cut utilizes most of the original shape of the rough diamond and the weight loss from cutting is low. As a result, its price is usually more attractive than a comparative round cut with the same weight.
This is a square or rectangular cut with numerous sparkling facets. It is a relatively new cut and often finds its way into solitaire engagement rings. Flattering to a hand with long fingers, it is often embellished with triangular at its sides. Because of its design, this cut requires more weight to be directed toward the diamond's depth in order to maximize brilliance. Depth of 70% to 78% are not uncommon.
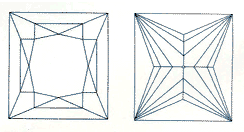 Most square or rectangular cuts just don't live up to the round brilliant for sparkle, but the Princess Cut was designed for getting maximum brilliance from a square cut.
Most square or rectangular cuts just don't live up to the round brilliant for sparkle, but the Princess Cut was designed for getting maximum brilliance from a square cut.
Always ensure that the setting for your princess cut diamond protects the four pointed corners -- these are the points most likely to chip (and why most rectangular or square diamond cuts have cropped corners).
Length to width ratio: A princess cut with a length to width ratio of less than or equal to 1.05:1 will appear square to the observer. While a squarer diamond is the preference of many, some people prefer a slightly rectangular-shaped princess diamond.
 Round diamonds are the most popular of all the shapes, perhaps because their circular proportions display the most "fire" and reflect more light back to the observer than any other shape. Round diamonds require that more rough be removed during cutting and polishing than with other shapes. The combined popularity of round diamonds and the significant weight loss during cutting are the two main contributing factors to the relatively higher price of these stones.
Round diamonds are the most popular of all the shapes, perhaps because their circular proportions display the most "fire" and reflect more light back to the observer than any other shape. Round diamonds require that more rough be removed during cutting and polishing than with other shapes. The combined popularity of round diamonds and the significant weight loss during cutting are the two main contributing factors to the relatively higher price of these stones.
 This shape has set the standard for all other diamond shapes, and accounts for more than 75% of diamonds sold today. Its 58-facet cut, divided among its crown (top), girdle (widest part)
This shape has set the standard for all other diamond shapes, and accounts for more than 75% of diamonds sold today. Its 58-facet cut, divided among its crown (top), girdle (widest part)
Wearing of Gem according to the Month in which they born Wearing of Gem according to the Month in which they born
| From & To | Lord Of The Month | Gem To Wear | Finger To Wear |
| 15th January to 15th February | Saturn | Blue Sapphire | Middle finger |
| 15th February to 15th March | Saturn | Blue Sapphire | Middle finger |
| 15th March to 15th April | Guru | Yellow Sapphire | Point finger |
| 15th April to 15th May | Kuja | Coral | Ring finger |
| 15th May to 15th June | Sukra | Diamond | Ring finger |
| 15th June to 15th July | Budha | Emerlad | Little finger |
| 15th July to 15th August | Chandra | Pearl | Ring finger |
| 15th August to 15th September | Ravi | Ruby | Ring finger |
| 15th September to 15th October | Budha | Emerlad | Little finger |
| 15th October to 15th November | Kuja | Coral | Ring finger |
| 15th November to 15th January | Guru | Yellow Sapphire | Point finger |
If you are born in these dates, I hereunder give the Lord of the Number and ruling Star and I recommend the gems to wear.
| DATE OF BIRTH | LORD OF NUMBER | RULING STAR | RECOMMENDED GEM |
| 1,10,19,28 | RAVI | Krutrika, Uttara,Uttarashada | Ruby |
| 2,11,20,29 | CHANDRA | Rohini, Hasta, Sravanam | Pearl |
| 3,12,21,30 | GURU | Punarvasu,Visakha,Poorabhadra | Yellow Sapphire |
| 4,13,22,31 | RAHU | Arudra, Swati, Sasatbisham | Gomed |
| 5,14,23 | BUDHA | Aselesa, Jesta,Revati | Blue Sapphire |
| 6,15,24 | SUKRA | Bharani,Pubba,Poorvashada | Diamond |
| 7,16,25 | KETU | Aswani,Makha,Moooa | Cat's Eye |
| 8,17,26 | SANI | Pushami,Anoorada,Uttarabhadra | Blue Sapphire |
| 9,18,27 | KUJA | Chitta, Mrugasira,Dhanista | Coral |
In Our Universe, Human Beings Actions Are Controlled By The Planetary System .If In Any Individual Horoscope, The Planets Are Well Placed He Will Be In Excellent Position Else Different. To Ward Off The Negative Effects, Gems Plays An Important Role.
Human Body Emits Radiations and Also Receive Radiations From The Universe. Depending Upon The Gravity, We Act Either Positively Or Negatively. If Any One Acts Negatively, Gem Therapy Is One Of The Best Method To Nullify The Negative Effects. Gems Increase Powers Of An Individual And Warding Off The Ill Effects Of The Planets. Selection Of Gems Is One Of The Most Important Factor And To Be Fixed In Right Metal To Gain Positive Results Else Negative Results Will Be There.
Gems Have Magnetic Powers And Emit Vibrations Which Have Strong Influence On Human Body. The Gems Before Wearing Should Be Energized Properly To Receive Positive Results.
Gems Have A Direct Impact On Individual Zodic Sign And Hereunder We Give Necessary Gems To Wear But Before Wearing The Gem, Every Care Has To Be Taken Of Individual Horoscope.
| Zodic Sign | Gems Suitable |
| Aries | Ruby, Blood Stone |
| Tarus | Golden Topen, Emerald Or Yellow Topaz |
| Gemini | Crystal |
| Cancer | Emerlad, Moonstone |
| Leo | Ruby |
| Vigro | Zircon, Turquoise |
| Libra | Diamond |
| Scorpio | Topaz Or Agate |
| Sagittarius | Amethyst |
| Capricorn | Smoky Quartz |
| Aquarius | Blue Sapphire |
| Pisces | Diamond |

Emerald Care:
As is the case with all jewelry, dirt and grime can collect on your emeralds over time from normal wear. This surface dirt steals away the beautiful color and brilliance you wear them for.
Here are a few simple guidelines to follow to help keep your emeralds as stunning as possible:


Cut
The quality of the cut plays an important role in assessing a stone's value, but it is not an exact science. There is no single cut that is valued more than another, but well cut, matched pairs and sets will cost more because of the difficulty in finding and cutting multiple stones to match not only in color, but size and overall appearance.
Different gemstones may sometimes have certain cuts associated with that gem. For example, you will often see diamonds in a round brilliant cut or a princess cut. Emeralds are no different in that regard, with the emerald cut being by far the most common. There are reasons for this, as you will read about in the next paragraph. But overall, the most common cuts in which you will find emeralds are: emerald cut, round and oval cuts, pear or teardrop cut, and cabochon. To a lesser extent you will find princess cuts, brilliants, trilliants, and various fancy cut variants to include hearts and carvings. Some of these cuts are rather self-explanatory, so we'll only comment further on those that are not as obvious.
The emerald cut may be square or rectangular in shape and is easily recognizable by its shape, large face, and chopped corners. It is used so often for emeralds that it took its name from them. A big reason why emerald cuts are so common for emeralds is that it yields more saleable product from the rough crystal. This is an important consideration because a significant portion of the rough crystal is already lost in the cutting process... Approximately thirty percent. When this cut is used on any other gemstone, it is still referred to as an 'emerald cut'.
Cabochon is an ancient cut that has a convex, rounded surface that is polished. Finer stones are not often cut in the cabochon style, but do turn out to be quite elegant when they are. Cabochons are not as brilliant as other cuts, but instead project a quiet, tasteful beauty that features the stones natural color. Other gemstones use the cabochon cut more frequently with great results. Notable examples are: cat's eyes (chrysoberyl), star rubies and sapphires, many opaque stones such as opal, turquoise, and moonstone.
Fancy cut is a term that may be used to describe custom carving-type cuts or non-typical cuts which would often be used for custom settings. Gem cutters, will inevitably cut unusually shaped stones to make the most of the gem crystal they have to work with. But for a dealer, carrying a large inventory of unusually cut stones is probably unwise. If a client plans to make a custom piece of jewelry, it may be unlikely that the design could incorporate the fancy cuts you'd have on hand. Because there will inevitably be these fancy cut stones produced and with perhaps a much less predictable demand, the prices of these stones will often be lower than if they were cut in the typical shapes. Herein lies opportunity. A savvy buyer, who may be looking create a custom-made piece, could find some real bargains. They would just have to be willing to work with what's available.

When someone speaks of diamonds, they often mention the "4 C's" of Color, Cut, Clarity, and Carat when they assess the quality and value of the stone. All of these characteristics are considered when one looks at an emerald, but they looked at in a much different way. For most colored stones, the most important trait, by far, is color. This is one reason why Colombian emeralds are more highly prized over all others. Their rich and superior green to bluish green colors are unparalleled by emeralds from any other source. This is the 'trademark' color for which Colombian emeralds are known, but the color range for Colombian stones is actually quite varied, even within the same mine. You'll find Colombian emeralds with colors that range from a pale yellow green to a dark blue-green that's almost surreal. Or from a bright grassy color to a milky green jade-like appearance. You get the idea...They vary a great deal, but they are easily recognized if placed amongst emeralds from other countries. Valuation differences will also be just as obvious. But as the old rule says...you get what you pay for.
Color is one of the most important considerations in buying an emerald. The richer greens and blue-greens tend to be the most expensive and highly regarded emerald colors, but this should never sway you from buying a lighter colored stone that you fancy. After all, beauty is very subjective. It is not determined by some arbitrary quality standard or grading system, but by how you feel about it. If you think it's beautiful.. that's all that matters. We receive just as many questions about our lighter colored stones as we do for some of the more expensive specimens with deeper color.
An interesting fact on the subject of color that we have to mention is that the beautiful rich blue-green color that you may see in some Colombian emeralds is almost certainly indicative that it comes from the famed Muzo mine. This mine is perhaps the most well known gem-producing mine in the world. Its name is synonymous with the outstanding quality emeralds it produces.

VARIETIES
Colombian Emerald - Emerald stone from Colombia. This emerald is usually of exceptional quality.
 Brazilian Emerald - Emerald from Brazil. The Brazilian emeralds are generally a lighter color than the Colombian emeralds.
Brazilian Emerald - Emerald from Brazil. The Brazilian emeralds are generally a lighter color than the Colombian emeralds.  Zambian Emerald - Quality emerald from Zambia.
Zambian Emerald - Quality emerald from Zambia.  Trapiche Emerald - Emerald with black impurities in the form of a six-rayed star.
Trapiche Emerald - Emerald with black impurities in the form of a six-rayed star.  Cat's Eye Emerald - Emerald exhibiting cat's eye effect. Cat's eye emerald is very rare, and only exists on paler emeralds.
Cat's Eye Emerald - Emerald exhibiting cat's eye effect. Cat's eye emerald is very rare, and only exists on paler emeralds.

 Pearl is a hard and rounded object produced by mollusks like pearl oysters. The unique luster of this gemstone depends on the reflection and refraction of light from the translucent layers. It is generally white but sometimes creamy or pinkish tinge. It may also be tinted with yellow, green, blue, brown, purple or black.
Pearl is a hard and rounded object produced by mollusks like pearl oysters. The unique luster of this gemstone depends on the reflection and refraction of light from the translucent layers. It is generally white but sometimes creamy or pinkish tinge. It may also be tinted with yellow, green, blue, brown, purple or black.